Cookie preferences
Choose which categories you allow. Necessary cookies are always on.
Plasma 101
Who: Eligible donors between 18 and 64 can earn up to $560 a month in NY and up to $770 a month in FL.
What: Plasma is the yellow part of your blood that replenishes naturally.
Where: Queens, Brooklyn, The Bronx (NY), and Ft. Pierce (FL).
Why: Get paid to donate and help treat bleeding disorders, immune deficiencies, and more.
When: No appointment needed—walk in anytime before closing.
Autologous Plasma: Healing from Within

Autologous Plasma: Healing from Within
Harnessing the body's own healing powers, autologous plasma therapy injects patients with their own blood plasma to accelerate injury recovery and regenerate tissue. This guide explains the science behind plasma's regenerative capacity, its expanding medical uses, and key benefits and limitations to consider when assessing treatment options. This guide explores plasma's promise in restoring health from within.
Overview of Autologous Plasma Therapy:
Title | Description |
What is Autologous Plasma? | Plasma taken from an individual's own blood, used to promote healing. |
Composition of Plasma | Contains water, proteins, minerals, platelets, clotting factors, immunoglobulins, albumin, and fibrinogen. |
Role of Platelets and Growth Factors | Platelets aid in clot formation and release growth factors like PDGF, TGF-β, VEGF, and IGF, which stimulate tissue repair. |
Extraction and Preparation | Blood is drawn and centrifuged to separate plasma, sometimes concentrated to form platelet-rich plasma (PRP). pH is normalized before injection. |
Medical Uses | Used in orthopedics, sports medicine, dermatology, cosmetic procedures, and dental/maxillofacial surgery for healing and regeneration. |
Benefits | Reduces risk of immune rejection, concentrates healing compounds, and jumpstarts regenerative mechanisms. |
Risks and Limitations | Minimal risks from injection procedure; efficacy varies by condition and severity. |
Understanding Autologous Plasma
Autologous plasma is plasma taken from a person's own blood and then re-administered to promote healing. Understanding the science behind autologous plasma highlights its unique composition and properties that make it a versatile therapeutic tool.
The Science of Plasma and Its Components
Plasma makes up over half of our blood volume. It is a straw-colored fluid containing water, proteins, minerals, and other dissolved components. Key ingredients in plasma are platelets, clotting factors, immunoglobulins, albumin, and fibrinogen.
Platelets are cell fragments vital for clot formation and releasing growth factors that signal tissue repair. When a blood vessel gets injured, platelets rush to the wound, stick together, and release these growth factors. Major growth factors from platelets are platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and insulin-like growth factor (IGF).
Growth factors then trigger local mesenchymal stem cells to multiply and mature into specialized cells needed for healing injured tissue. Other plasma components, like cytokines, also help coordinate the inflammatory response. Plasma contains an array of biologically active compounds that can profoundly support healing and recovery.
Extraction and Preparation of Autologous Plasma
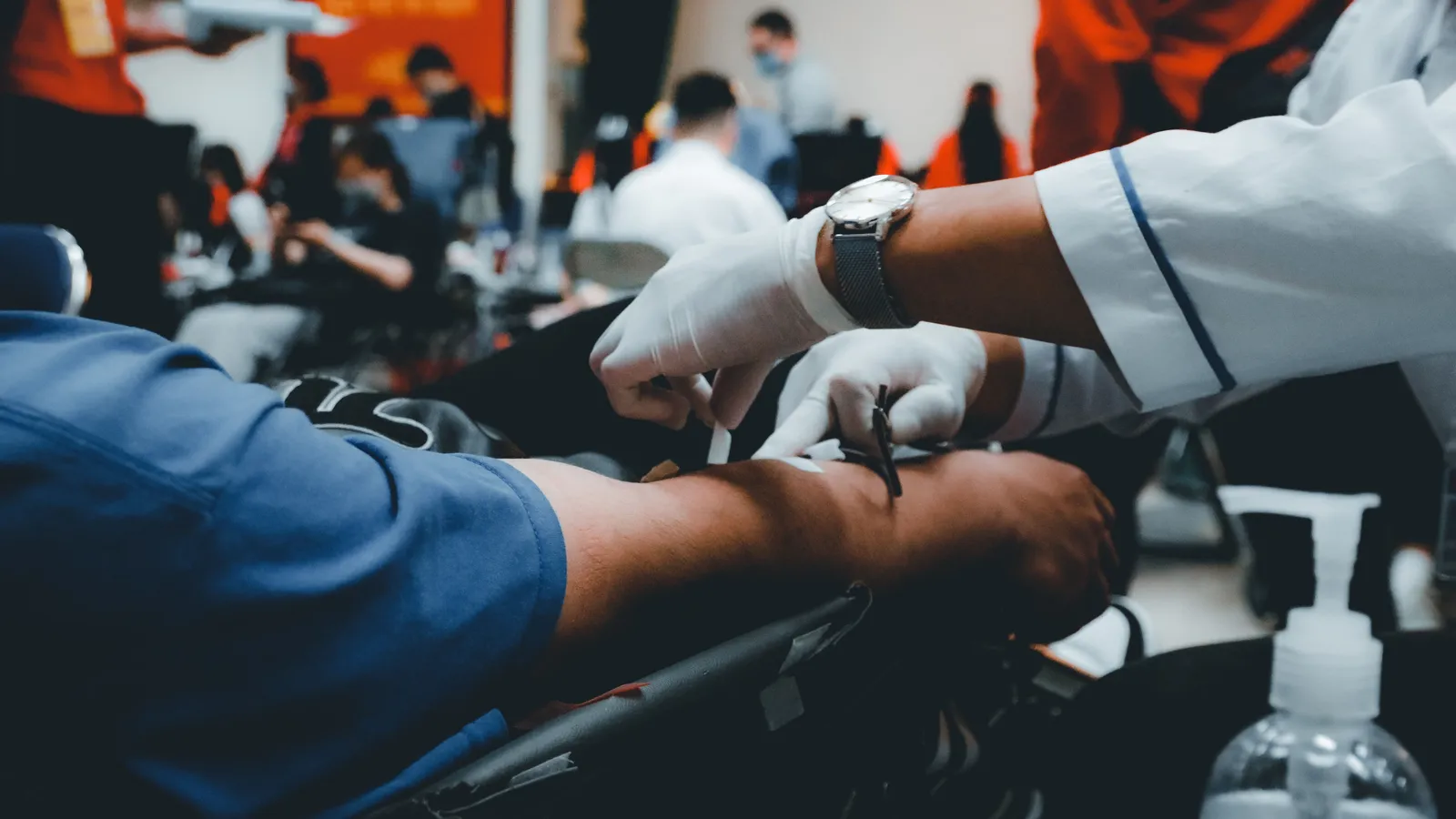
To obtain autologous plasma for medical use, blood is directly drawn from the patient’s arm. Next, the blood goes into a centrifuge, a machine spinning the blood at high speeds to separate its components by density. Red blood cells are densest and spin down to the bottom of the tube. The straw-colored plasma stays at the top, which then gets extracted.
Sometimes the process involves an extra spin cycle to concentrate platelets, yielding platelet-rich plasma (PRP). PRP has a super-charged growth factor content to amplify the healing response. Doctors can also tune the platelet concentration higher or lower depending on the condition being treated.
Before injection, the final autologous plasma preparation gets buffered to normalize its pH. Preparations like PRP also require activation shortly before application. This releases growth factors from platelets already primed to initiate tissue repair. The activated plasma then gets directly applied to the treatment area.
Though the equipment and techniques to produce PRP seem high-tech, the basic principle is using concentrated healing factors naturally occurring in patients’ own blood. Harnessing the regenerative capacity intrinsic to our blood via plasma therapy constitutes a huge advance in regenerative medicine, and plasma therapy is changing medical treatment.
Olgam Life specializes in collecting plasma that is vital for creating life-saving therapies if health issues arise requiring autologous plasma therapy. Their donor centers provide a friendly, high-quality environment for community members to supplement their income through regular plasma donations. These centers act as local hubs, facilitating plasma collection critical for life-saving medical treatments.
Applications and Implications of Autologous Plasma Therapy:
Title | Description |
Orthopedics and Sports Medicine | Treats acute joint injuries and chronic conditions like tennis elbow, accelerating healing and reducing pain. |
Dermatology and Cosmetic Procedures | Used in skin resurfacing and treating acne scars, promoting collagen remodeling and skin rejuvenation. |
Dental and Maxillofacial Surgery | Enhances bone graft integration and osseointegration in dental implants, shortening healing time. |
Advantages in Treatment | Autologous nature reduces immune reactions, tailored growth factor concentration for specific conditions. |
Procedural Risks | Risks of infection or structural damage from needle injections, mitigated by ultrasound guidance. |
Efficacy Considerations | Varies based on injury type and severity; not a cure-all but offers significant benefits in many cases. |
Safety and Tolerability | Generally safe with minimal side effects; considerations for patients on blood thinners or with bleeding disorders. |
Uses of Autologous Plasma in Medicine
The multitude of biologically active compounds in autologous plasma enables wide-ranging therapeutic applications across medical specialties. Understanding some specific ways plasma improves patient outcomes sheds light on this valuable healing adjunct.
Autologous Plasma in Orthopedics and Sports Medicine
In orthopedics, autologous plasma injections treat acute joint injuries like MCL sprains or partial tendon tears by delivering concentrated growth factors to sharply accelerate healing. This faster recovery gets athletes resuming intense training sooner. For chronic injuries like tennis elbow tendinosis, plasma reactivates the body’s regenerative repair processes. Tennis players report significantly reduced elbow pain and fewer recurrences with PRP injection regimens.
Osteoarthritis and cartilage defects causing debilitating knee pain also respond well to precisely targeted injections of platelet-rich plasma (PRP). The flood of cell signaling proteins stimulates local cartilage progenitor cells to regenerate hyaline cartilage. Patient function dramatically improves as this smooth, lubricated cartilage coating cushions the bones of the knee joint.
By using healing factors sourced from patients themselves, autologous plasma avoids risks like immune responses to infections or disease transmission from donor products. This makes it a versatile treatment for frequently injured load-bearing joints. Olgam Life’s community plasma collection centers help maintain local access to this regenerative therapy benefitting many active patients.
Autologous Plasma in Dermatology and Cosmetic Procedures
In aesthetic dermatology, the fractional CO2 laser resurfacing technique removes skin damaged by sun exposure and aged by time to reveal fresher skin below. This ablative technique prompted the development of non-ablative erbium plasma skin resurfacing.
By spraying a plasma spark shower onto the skin instead of burning it, surface imperfections get erased by active dermal remodeling below. Patients enjoy comparable skin rejuvenation and tightening without the pain and lengthy recovery from laser wounds.
For specifically targeting acne scars, autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections directly into scar tissue produce marked improvements. The activated growth factors accelerate fibroblast activity to remodel collagen. Indenting, atrophic scars progressively elevate to become flush with the surrounding skin. Repeated PRP treatments continue improving scar appearance with minimal discomfort and no downtime for patients.
Autologous Plasma in Dental and Maxillofacial Surgery
Dentistry utilizes platelet-rich plasma to optimize treatment outcomes. Following tooth extractions in preparation for dental implants, sockets often require bone grafting to reconstitute lost volume. Mixing PRP into the bone graft accelerates the graft’s integration into natural bone to shorten healing time. This allows placing the dental implant sooner.
For implant placement itself, applying PRP into the surgical site before closing the gums promotes faster osseointegration between the titanium implant surface with regenerating bone. This durable connection then securely anchors the lifelike dental crown attached later. Using growth factors intrinsic to patients’ own blood enables cutting-edge plasma-assisted dental treatments.

The Benefits and Risks of Autologous Plasma Therapy
Harnessing the body's innate capacity to heal itself, autologous plasma therapy offers clear advantages but also limitations to consider when assessing treatment options. Analyzing the risk-benefit profile sheds light on the most responsible, effective applications of this emerging biologic technology.
Advantages of Using Autologous Plasma
The primary benefit of autologous plasma is having no risk of immune rejection since it comes from the patient's own body. Transfusions of donor plasma run the risk of inducing reactions against foreign proteins. But with autologous plasma, compatibility issues causing treatment failures or adverse effects essentially become non-concerns.
Additionally, plasma contains a host of growth factors and signaling plasma proteins highly adapted to cue repair pathways in that individual. Concentrating these endogenous healing compounds via centrifugation and applying them back to sites of injury or degeneration jumpstarts the body’s innate regenerative mechanisms.
These major advantages of reduced immunogenicity paired with personalized, physiologic regeneration make autologous plasma a preferential treatment for many orthopedic, dermatologic, dental, and cosmetic applications. Olgam Life has numerous locations and provides an essential community service by collecting plasma used to create treatments for patients worldwide.
Potential Risks and Limitations
While extremely safe regarding infectious disease transmission and immunologic reactions, autologous plasma does carry risks from the injection procedure itself. Though quite minimal, any needle injection risks introducing infection or damaging structures like nerves or blood vessels. However, ultrasound guidance during injection greatly mitigates these procedural risks.
Regarding treatment efficacy, some conditions respond better to plasma therapy than others. For acute injuries like ligament tears, autologous plasma clearly accelerates healing. But for severely arthritic joints that have lost cartilage cushioning, injections bring only temporary relief of symptoms. Similarly, plasma rejuvenates aged or scarred skin but cannot recreate youth. So efficacy differs depending on disease treatment aims and disease severity.
While plasma presents fewer risks than many anti-inflammatory drugs, some patients may experience mild local reactions like swelling or bruising. Also those taking blood thinners or with bleeding disorders require special consideration. So a thorough health assessment helps identify individuals unlikely to tolerate injections well or safely.
With an excellent short-term safety profile and clear healing benefits for many indications, autologous plasma therapy continues gaining clinical adoption. Further studies quantifying long-term outcomes will refine application guidelines. But powerful treatment benefits for many currently outweigh the low risks.
Read our frequently asked questions to find out more about what to expect from plasma donation. If you can’t find the information you’re looking for, why not give us a call?