Plasma 101
Who: Eligible donors between 18 and 63 can earn up to $560 a month in NY and up to $770 a month in FL.
What: Plasma is the yellow part of your blood that replenishes naturally.
Where: Queens, Brooklyn, The Bronx (NY), and Ft. Pierce (FL).
Why: Get paid to donate and help treat bleeding disorders, immune deficiencies, and more.
When: No appointment needed—walk in anytime before closing.
Platelet Rich Plasma: A Revolution in Regenerative Medicine

Platelet Rich Plasma: A Revolution in Regenerative Medicine
Suffering from nagging joint pain or stubborn injuries that won’t heal? Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy represents an exciting innovation in regenerative medicine using the body’s own healing factors. This article explains how PRP leverages your blood’s growth properties to reduce inflammation, relieve arthritis, accelerate injury recovery, and drive scarless tissue repair through natural processes. Read on to discover the current and future therapeutic applications of PRP in orthopedics, dermatology, aesthetics, dentistry and beyond.
Platelet-rich plasma harnesses growth factors from blood to treat injuries, arthritis, and wrinkles. Still early research, but shows promise revitalizing tissue by reducing inflammation and stimulating localized cellular healing.
Basics and Biological Mechanism of PRP:
Title | Description |
What is PRP? | Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a concentration of platelets in plasma, typically 2-8 times greater than in normal blood. It's produced by processing a person's own blood to concentrate platelets. |
Extraction Process | Involves collecting blood and using a two-step centrifugation process to separate red blood cells and concentrate platelets in plasma. |
Platelet Concentration | PRP concentrations range from 1-2 million platelets per microliter, compared to 150,000-350,000 in normal blood. |
Biological Mechanism | PRP's concentrated platelets release growth factors essential for inflammation modulation, cellular migration, and tissue regeneration. |
Key Growth Factors | Includes PDGF, TGF-β, VEGF, bFGF, and EGF, which coordinate to stimulate localized healing and tissue regeneration. |
Healing and Regeneration | PRP stimulates localized tissue healing and regeneration through coordinated cellular interactions and responses. |
What is Platelet Rich Plasma?
Understanding the Basics of PRP
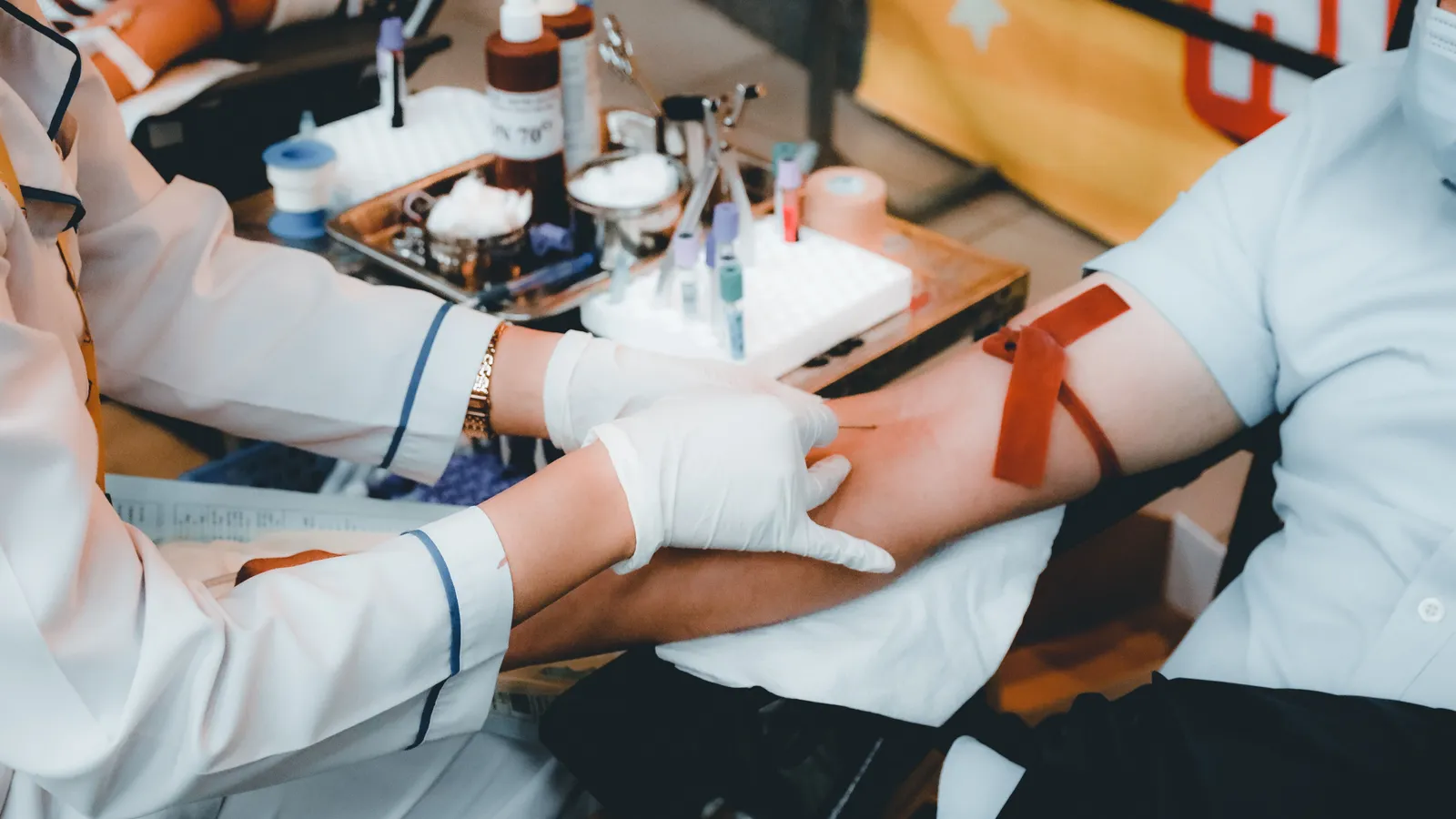
Platelet-rich plasma, commonly known as PRP, is an autologous concentration of platelets in a small volume of plasma. To produce PRP, a sample of a person's own blood is taken and processed to separate out the plasma, which contains the platelets. This plasma then undergoes further processing to concentrate the platelets to higher levels than what is typically found in normal blood. The final PRP preparation contains a platelet concentration that is typically 2-8 times greater than baseline, as well as increased amounts of several growth factors.
The extraction process for PRP begins by collecting blood from the patient. This whole blood then undergoes a two-step centrifugation process to first separate out the red blood cells, and then concentrate the platelets in a small volume of plasma. The final preparation contains this platelet-rich plasma suspension in 5-10mL of plasma. Compared to normal blood levels of around 150,000-350,000 platelets per microliter, PRP concentrations usually range from 1-2 million platelets per microliter.
The Biological Mechanism of PRP
The highly concentrated platelets contained in PRP allow it to play an important role in healing and tissue regeneration processes in the body. When platelets become activated, they release alpha granules that contain numerous growth factors and other molecules essential for modulating inflammation, stimulating cellular migration and proliferation, as well as regulating the formation of new blood vessels and tissue matrix components.
Some key growth factors contained in PRP include platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), basic fibroblast growth factors (bFGF), and epidermal growth factors (EGF). These molecules all coordinate to stimulate localized healing mechanisms when PRP is introduced into tissues.
For example, PDGF encourages fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells to multiply and lay down extracellular matrix. TGF-β plays a key role regulating the inflammatory response as well as driving collagen production. VEGF and bFGF promote angiogenesis, which restores circulation to damaged tissues. Meanwhile, EGF assists in stimulating cellular proliferation and regeneration.
The concentrated growth factors work synergistically to modulate inflammation at the site of injury, while also signaling various cell types to migrate into the area to assist in regeneration efforts through proliferation, secretion of healing molecules, and tissue remodeling. Through these coordinated cellular interactions and responses, PRP is able to stimulate localized tissue healing and regeneration.
Applications of PRP in Medicine:
Title | Description |
PRP in Orthopedics | Used for treating knee arthritis, partial ACL tears, rotator cuff repair, patellar tendinitis, and Achilles tendonitis. Reduces inflammation and promotes tissue regeneration. |
PRP in Dermatology | Supports wound healing and recovery, treats acne scars, and stimulates hair growth. Increases collagen production and rejuvinating skin, veins, and hair follicles. |
PRP in Cosmetic Surgery | Used for facial rejuvenation, breast augmentation, and hair restoration. Combines with other treatments for improved results. |
PRP in Dentistry | Assists in gum disease treatment, bone regeneration, and healing post-extraction. Used in maxillofacial surgery for bone loss and wound healing. |
Future of PRP Therapy | Research is exploring combinations with stem cell therapies and 3D bioprinting for enhanced outcomes. Focus on sustained-release formulations and growth factor profiling. |
Challenges and Considerations | Includes standardization of preparation protocols, regulatory policies, and ethical considerations in commercialization and clinical use. |
The Uses of Platelet Rich Plasma in Medicine
PRP in Orthopedic Treatments
If you're one of the millions suffering from bothersome knee arthritis pain or that lingering tennis elbow, you may have heard your orthopedist mention platelet-rich plasma. Beyond injuries, PRP is gaining popularity as an effective treatment for many common orthopedic conditions.
Let's quickly recap - PRP harnesses your body's own healing factors concentrated from blood to stimulate tissue regeneration. How's it work for bones and joints? Say you have moderate knee arthritis and walking up stairs causes a nagging ache. Injecting that concentrated mix of growth hormones into the joint kickstarts crucial repair cells like cartilage progenitors and bone marrow stem cells to get to work reducing inflammation and rebalancing joint tissue.
Over a period of weeks to months, patients find swelling goes down as new smooth cartilage covers worn bone ends. Numerous studies now back PRP injections as an arthritis relief strategy, with reductions in pain lasting over a year based on clinical scales and imaging confirming regenerative structural changes inside joints.
Beyond osteoarthritis, PRP is making strides with injuries like partial ACL tears, rotator cuff repair after surgery, patellar tendinitis ("jumper's knee") and Achilles tendonitis in athletes. For nasty elbow tendon pain from tennis, compared to steroids, single or few shots of PRP may relieve elbow pain for over 6 months by promoting real tendon healing.
Though more trials are needed, current evidence and mechanisms supporting tissue regeneration place PRP among leading biologic treatments for musculoskeletal problems.
PRP in Dermatology and Skin Care
Got acne scars or thinning hair you want to fix without surgery? Dermatologists turn to plasma rich in youthful growth factors to rejuvenate aging skin and enhance wound healing and recovery. When it comes to scars, combination laser and PRP skin needling notably boosts collagen production leading to great improvement within few monthly sessions.
And if your part seems wider lately or you just want thicker locks, studies show injecting activated plasma kickstarts shifts from hair follicle resting to active growing phases for new dense growth showing around 3 months in. Repeating injections further boosts hair density over time.
Research confirms plasma packed with tissue stimulating molecules can renew skin, veins and hair follicles by increasing plump matrix proteins like collagen and recruiting repair cells to where they’re needed. In sports medicine, PRP even helps stubborn ulcers heal when other treatments fail to meet skin grafting needs.
PRP in Cosmetic and Plastic Surgery
Good thing there are more options nowadays than the staple face lift, nose job or implant augmentation for cosmetic enhancements! Using innovative biologic solutions like platelet-rich plasma, plastic surgeons now provide one-stop bespoke solutions catered to unique needs.
Let's say you want subtler facial rejuvenation without radical surgery. Combining hyaluronic acid fillers with plasma fractions containing your own concentrated growth factors encourages new collagen for up to 9 months of smoother skin and relaxed wrinkles. Minimally invasive injections in an office visit makes this categories better than extensive surgery for many.
Even breast augmentation can skip implants as a thing of the past - by reinjecting patient's own fat cells enriched with PRP for better volume retention, this natural lift avoids reactions to foreign materials. One study found up to 90 mL graft maintenance at half a year mark, perfect for stable Cup size boost.
Hair restoration and fraction laser skin resurfacing also show marked improvements when combined with activated plasma elements that regenerate rather than simply mask aging. With myriad applications still being discovered, PRP holds promise as a versatile biotic adjuvant advancing modern cosmetic practice.
PRP in Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery
Don't be surprised next time your dentist suggests plasma therapy! Beyond deep cleanings and grafting for gum disease treatment, regenerative PRP injections can regenerate lost bone and attachment around teeth. Following extractions, preparing sockets by concentrating growth factors in patient's blood accelerates healing and preserves thickness for eventual implants compared to nothing.
This biologic innovation has also crept into maxillofacial, craniofacial and oral surgery specialty practice, especially where bone losses or wounds after cancer removal require reconstruction. Early evidence suggests plasma enriched with tissue stimulating factors may benefit such defects while reducing infection risks that often complicate head and neck surgery recoveries.
Though still investigational for oral rehabilitation, carrying Your own healing serum during procedures can certainly turbocharge recuperation over doing nothing. Sci-fi or not, cyborg PRP just may reform how we approach oral health and appearance enhancement care.

The Future of Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy
Emerging Trends and Research in PRP
As a relatively novel biologic treatment, the applications and therapeutic potential of PRP are still being actively researched and expanded. Exciting ongoing research is exploring combining PRP with stem cell therapies, extracellular matrix components, synthetic biomaterials and 3D bioprinting approaches for enhanced regenerative outcomes.
For example, early research on formulations incorporating PRP with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells show promise for bone defect repair and cartilage regeneration. Complementary effects may stimulate endogenous joint stem cells while delivered stem cells directly differentiate into cartilage. Such combination cellular therapies aim to further boost PRP’s regenerative mechanisms. Additionally, researchers are delving into the potential of plasma therapy in treating COVID-19, investigating its immunomodulatory effects and ability to aid in the recovery of patients affected by the virus.
Novel research also focuses on sustained-release PRP formulations for prolonged therapeutic effects. Incorporating platelet growth factors with hydrogels or microspheres allows for their controlled release over days to weeks upon injection into injury sites. These innovations may reduce need for repeat PRP injections in certain applications.
As research continues elucidating PRP’s mechanisms and clinical effects, growth factor profiling is also being incorporated to identify optimal PRP compositions for different tissue contexts. Overall these advances can tailor PRP specifically to applications where it shows maximal benefit.
Advancements in PRP Preparation and Application
Standardization in PRP preparation protocols across clinics has been a challenge facing the field. Research now focuses on streamlining production systems to improve PRP quality and performance. For example, innovations like the Harvest SmartPreP PRP kit allow for efficient, automated isolation of platelet fractions optimized for regenerative properties in under 15 minutes.
Targeted application techniques are also being developed, like kits for activated PRP gel matrices to retain growth factors locally within joints or surgical bone defects for sustained tissue regeneration. Adjuvant injectables like hyaluronic acid also show promise for modulating PRP effects.
Such technology refinements allow physicians easier access to quality treatment options while ensuring safety. They drive increased adoption in clinics to help patients benefit from PRP’s healing effects.
Potential Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Like any novel therapy, realizing the promise of PRP on a global scale requires confronting challenges around standardization, regulation policies and ethical application. For instance, many commercial PRP preparation systems exist without consensus on optimal protocols for factors like final platelet concentrations for particular indications.
Regulatory bodies are also still assessing appropriate classifications and guidelines for licensed PRP use. These determinations require balancing patient safety while enabling access to PRP therapies. Emerging evidence continues to inform such decisions.
Ethical considerations around commercialization and claims made without extensive clinical evidence are also relevant to discuss. Formulating clear guidelines for PRP use in untested applications and in restricted populations like elite athletes enhances ethical standards in the field.
Addressing these challenges through bodies like the International Cellular Medical Society can support valuable knowledge sharing. Ultimately regulatory frameworks must uphold efficacy and safety while enabling innovation of progressive regenerative tools like PRP.
To explore cutting-edge advancements in regenerative medicine and plasma therapies, give us a call! Olgam Life offers state-of-the-art treatment for donors while providing life-saving resources for the medical industry. Unlike many other plasma donation services, Olgam Life focuses solely on the aggregation aspect of the donation process, enabling us to focus more closely on the care our donors receive. Check out our locations.